Micro SD cards, despite their small size, store vast amounts of data. Their compact nature, however, makes them vulnerable to severe physical damage from drops, bending, snapping, or liquid exposure. Such events can render a MicroSD card unusable and unrecognizable by any device.
In cases of extreme physical damage, standard data recovery methods are impossible. Micro SD chip-off recovery, a highly specialized technique, then becomes the critical, often only, path to retrieving valuable files. This guide explains what chip-off recovery entails and why it requires expert handling.
What is Micro SD Chip-Off Data Recovery?
Micro SD chip-off data recovery is an advanced technique used when severe physical damage or electronic failure prevents normal access. It involves physically removing the NAND flash memory chip(s) from the damaged card’s board. Experts then use specialized readers to extract raw data directly from these chips, bypassing the failed components.
When is Chip-Off Recovery Necessary for Micro SD Cards?
This method becomes the primary or only option when communication with the NAND memory through the card’s normal interface is impossible. Key scenarios include:
Severe Physical Damage
- Cracked or Snapped Card: If the card’s body or internal circuit board (substrate) is physically broken, severing connections between the NAND chip, controller, and external contacts. (Related reading: Recovering Data from Broken Flash Media.)
- Connector Damage: If the gold contact pads are severely damaged, corroded, or ripped from the substrate beyond micro-repair capabilities.
Catastrophic Electronic Failure
- Dead Controller Chip: When the controller chip managing the NAND has completely failed and cannot be bypassed via firmware or other electronic means.
- Irreparable PCB Damage: Extensive corrosion (often from water damage) or electrical damage destroying critical pathways on the card’s internal board.
- Unrecoverable Firmware Corruption: In rare instances where the controller’s firmware is so corrupted it prevents any device communication (“bricking”) and cannot be repaired through specialized tools.
The technique relies on the NAND flash memory chip(s) themselves being physically intact. If the NAND chip is cracked or shattered, chip-off recovery is not possible.
When is Chip-Off Recovery Necessary for MicroSD Cards?
Chip-off recovery is typically the method of last resort, employed when the standard communication pathway through the card’s controller and external contacts is completely broken or unusable due to:
- Severe Physical Damage:
- Cracked or Snapped Card: If the plastic casing and internal substrate/PCB are broken, especially if the break separates the NAND chip from the controller or contact points. See our general guide on recovering data from broken flash media.
- Bent or Heavily Damaged Connectors: If the gold contact pads are ripped off or damaged beyond repair.
- Catastrophic Electronic Failure:
- Dead Controller Chip: If the controller chip itself has failed completely (e.g., due to electrical damage, internal fault) and cannot communicate with the NAND or the host device.
- Severe PCB Damage: Extensive corrosion (often from water damage or electrical damage (like a short circuit frying components) on the circuit board that prevents power or data signals from reaching the NAND chip via normal means.
- Unrecoverable Firmware Corruption: In rare cases where severe firmware corruption on the controller makes the card completely unresponsive (“bricked”) and standard firmware recovery tools fail.
In essence: Chip-off becomes necessary when the path to the data (the controller, PCB traces, connectors) is destroyed, but the NAND chip containing the data is believed to be physically intact.
Get a Free Consultation.
Our recovery experts are ready to assess your device and guide you through the safest path to recovery. Fill out the form to get started.
"*" indicates required fields
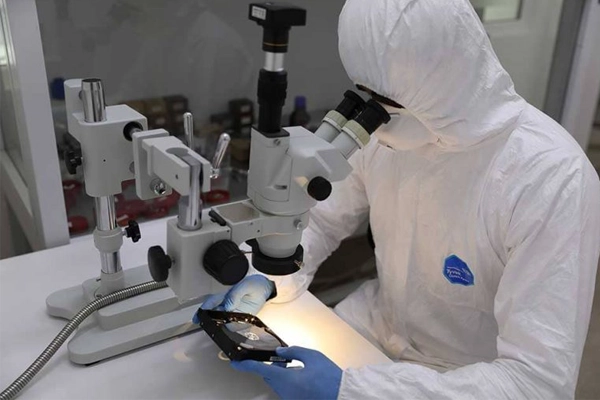
The Micro SD Chip-Off Recovery Process
This advanced procedure requires specialized equipment, a controlled environment, and expert technicians. It is absolutely not a DIY task.
Step 1: Extraction of the NAND Memory Chip
- Card Disassembly: The damaged MicroSD card’s outer casing (if present) is carefully removed or bypassed.
- Chip De-soldering/Removal: Using precision tools like heat guns, specialized solder stations, or sometimes micro-milling/grinding techniques under a microscope, the technician carefully removes the tiny NAND flash memory chip(s) from the MicroSD card’s substrate/PCB. This requires extreme care to avoid overheating or physically cracking the fragile NAND chip itself.
Step 2: Cleaning and Preparation
The removed NAND chip(s) often have residual solder or epoxy. They must be meticulously cleaned under magnification to expose the contact points (usually tiny balls or pads in a BGA – Ball Grid Array – pattern).
Step 3: Reading the Raw Data
- Specialized NAND Readers: The cleaned chip is placed into a specialized socket adapter compatible with its specific pinout and type (e.g., TSOP48, BGA152, etc.).
- Interfacing: This adapter connects to powerful NAND flash reader hardware/software systems. These systems communicate directly with the NAND chip, bypassing the original failed controller.
- Raw Dump: The reader extracts the entire raw binary data stored on the chip(s), creating a “raw dump” image file on a secure workstation. This can take significant time depending on the chip size and condition.
Step 4: Data Reconstruction and Reassembly
Extracting the raw data is only half the battle. The data dump is not a usable file system; it’s scrambled according to the algorithms used by the original controller chip.
- Identifying Controller Algorithms: Experts must determine how the original controller organized data (e.g., XOR patterns, interleaving, wear leveling, error correction code – ECC). This often requires databases of known controller behaviors or complex analysis.
- Software Reconstruction: Specialized software applies the identified algorithms in reverse to unscramble the raw data, correct errors where possible, and rebuild the original file system structure (FAT32, exFAT).
- File Extraction: Once the file system is virtually rebuilt, the user’s files and folders can be extracted and saved to new, healthy media.
This complex reconstruction phase is a key part of our overall data recovery process.
Is Chip-Off Recovery Always Successful?
Chip-off recovery success is not guaranteed. It depends primarily on the physical condition of the NAND memory chip itself. If the NAND chip is cracked, shattered, or internally shorted due to the initial damage, data retrieval is impossible. Success also relies on overcoming complex controller algorithms and potential encryption during data reconstruction.

DIY Recovery
Risks permanent data loss
Let the Specialists Handle It
DIY attempts often result in permanent data loss. Our certified recovery specialists use advanced tools in controlled environments for the highest success rate.

24/7 Emergency Service
Challenges and Limitations
Key challenges include:
NAND Chip Integrity: As mentioned, physically damaged NAND makes recovery impossible.
Monolithic Drives: Many modern tiny flash devices integrate components into one block, requiring different complex techniques (like pinout discovery via grinding) instead of chip removal. Learn about monolithic flash drive recovery.
Encryption: Controller-based hardware encryption can make reconstructing data from raw NAND dumps extremely difficult or impossible without specific keys or methods.
Complex Controllers: Proprietary or poorly documented controller algorithms complicate data reassembly.
Certified & Trusted Data Recovery
PITS Data Recovery possesses the advanced BGA rework stations, specialized NAND readers, and expert engineering knowledge required to perform successful Micro SD chip-off recovery.







When Chip-Off is the Appropriate Solution
Consider this service if your MicroSD card:
- Is physically broken (snapped, cracked).
- Has severely damaged connectors.
- Is completely unresponsive/undetected after severe water or electrical damage.
- Has been diagnosed by a professional as having a non-recoverable controller or PCB failure where the NAND chip is likely intact.
What To Do:
- Collect All Pieces: Carefully gather all fragments of the broken card.
- Do Not Attempt DIY: Do not try to glue, tape, or read damaged cards.
- Contact PITS Data Recovery: Explain the physical condition clearly. We can assess if chip-off is a viable option based on your description and subsequent lab evaluation.
Don't Let Data Loss Ruin Your Business
Minimize business disruption. We retrieve lost data fast, so you can focus on what matters.
Conclusion
MicroSD chip-off recovery is a highly advanced method used when standard techniques fail due to severe physical or electronic damage. By removing and directly accessing the NAND flash memory chip, specialists can often retrieve data even from cards suffering catastrophic failures.
Though complex and requiring specialized equipment, chip-off recovery can successfully recover data from MicroSD cards once considered beyond repair. If your card is critically damaged, PITS Data Recovery offers the expertise and technology needed for advanced recovery.
Explore: SD Card Data Recovery Services.